In today’s textile and manufacturing industries, the materials we choose shape not only the quality of the products we use but also the impact on the planet. Among the most widely discussed fibers are polyester fiber and rPET fiber. While polyester has long been a dominant choice in fabrics and packaging, the growing awareness of sustainability has pushed recycled alternatives like rPET into the spotlight.
If you’ve ever wondered how rPET fiber compares to traditional polyester fiber, this guide will break it down for you.
What is Polyester Fiber?
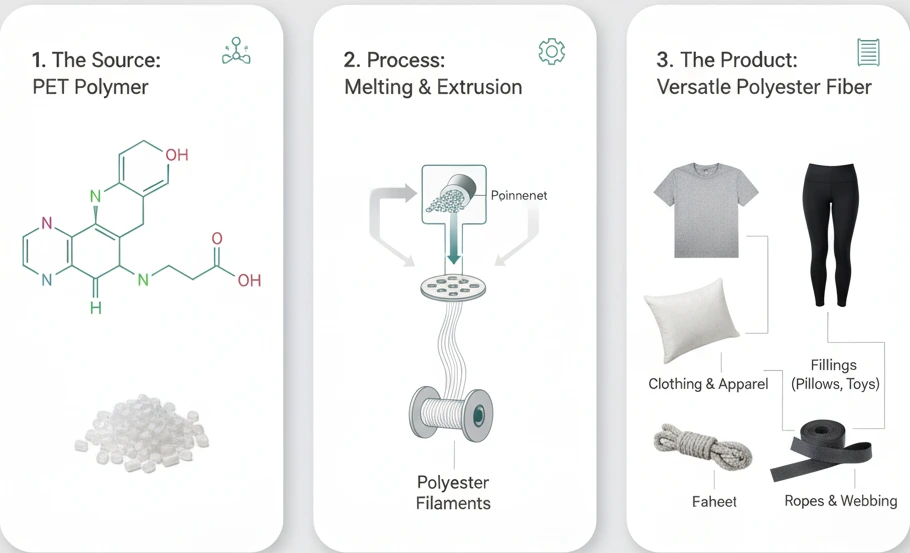
Polyester is one of the most common synthetic fibers used around the world. It is made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a type of plastic derived from petroleum. This makes polyester a non-renewable resource-based product, yet one that offers impressive durability and affordability.
The manufacturing process involves polymerization of PET, which is then spun into poly fabric threads. These are used to make polyester fabric material for clothing, upholstery, home décor, and even industrial applications.
Key benefits of polyester fiber include:
-
High durability and wrinkle resistance
-
Cost-effectiveness compared to natural fibers
-
Quick-drying and easy-care properties
Because of these advantages, polyester remains one of the most widely used fabrics across industries.
What is rPET Fiber?
rPET fiber stands for recycled polyethylene terephthalate fiber. It is produced by recycling PET waste mainly plastic bottles, food containers, and industrial PET scraps. Instead of being discarded in landfills or polluting oceans, this plastic waste is collected, cleaned, and transformed into usable fiber.
The recycling process involves shredding PET into flakes, melting them, and re-spinning them into fiber. The result is a material that closely resembles virgin polyester but comes with significant environmental benefits.
Why rPET matters:
-
It reduces plastic waste
-
It saves energy compared to producing new polyester
-
It supports circular economy models
-
It provides sustainable raw materials for textiles and packaging
Applications of rPET fiber include fashion, footwear, home furnishings, and eco-conscious packaging solutions.
rPET Fiber vs Polyester: A Detailed Comparison

1. Origin & Circularity
-
rPET fiber: Made from recycled PET waste, reducing the need for new raw materials. Supports a circular economy by turning waste into usable fiber.
-
Polyester (virgin): Made from new petrochemical resources, requiring fresh extraction of oil and natural gas.
👉 If sustainability is your goal, rPET has the advantage.
2. Environmental Footprint
-
rPET fiber: Produces significantly fewer greenhouse gases and requires less energy compared to virgin polyester production. Some studies report energy savings of up to 45–60%.
-
Polyester (virgin): Has a higher carbon footprint due to resource extraction and energy-intensive processing.
👉 For brands looking to cut emissions, rPET is a greener choice.
3. Performance & Durability
-
rPET fiber: When produced under strict quality control, rPET matches virgin polyester in strength, elasticity, and durability. However, poor-quality recycling processes may lead to slight variations.
-
Polyester (virgin): Consistently delivers strong and reliable performance thanks to controlled production conditions.
👉 For most everyday uses, rPET performs just as well as polyester.
4. Dyeing & Color
-
rPET fiber: May show color inconsistencies if made from mixed feedstock. Many manufacturers now offer pre-colored rPET fibers, which reduce dyeing costs and improve shade consistency.
-
Polyester (virgin): Offers excellent color uniformity, making it the standard for high-precision applications.
👉 rPET is catching up quickly with colored RPSF innovations.
5. Cost & Supply
-
rPET fiber: Historically more expensive due to recycling processes, but prices are becoming more competitive as demand grows.
-
Polyester (virgin): Typically cheaper and widely available.
👉 Cost-sensitive industries may still favor virgin polyester, but rPET is becoming economically viable.
6. Processing & Quality Control
-
rPET fiber: Requires strict sorting, cleaning, and testing to ensure consistent quality. Chain degradation can occur after multiple recycling loops.
-
Polyester (virgin): More consistent and predictable in processing.
👉 For technical or high-spec applications, virgin polyester may be preferable.
Key Differences Between rPET Fiber and Polyester Fiber
Although they share the same chemical base PET (polyethylene terephthalate) there are important differences between them.
| Feature | Polyester Fiber | rPET Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Made from virgin petroleum-based PET | Made from recycled PET bottles and waste |
| Sustainability | Non-renewable, high environmental impact | Eco-friendly, reduces waste and emissions |
| Durability | Highly durable, consistent performance | Nearly as durable, slight variations in strength |
| Cost | Generally cheaper due to large-scale production | Slightly higher due to recycling process |
| Applications | Clothing, upholstery, packaging | Sustainable fashion, green packaging, furnishings |
Is rPET Fiber as Good as Polyester?
One of the most common questions is whether rPET matches the performance of virgin polyester. The answer: yes, in most cases.
Both fibers share the same chemical composition, meaning their texture, appearance, and usability are nearly identical. rPET fiber may have minor variations in strength or feel depending on the recycling process, but these differences are often negligible.
For brands focused on sustainability, rPET offers an attractive balance between performance and responsibility.
Why Brands Are Choosing rPET Over Polyester
Global fashion and textile industries are under increasing pressure to reduce their environmental footprint. This has led many brands to adopt rPET fiber in place of virgin polyester fabric.
Reasons behind the shift:
-
Consumer demand: Eco-conscious buyers prefer sustainable fabrics.
-
Regulatory pressure: Governments worldwide are promoting recycling initiatives.
-
Corporate responsibility: Companies aim to reduce carbon footprints and align with sustainability goals.
Today, many global apparel brands proudly label their products as made with recycled polyester, signaling a shift toward circular production models.
Common uses of rPET and Polyester Fiber
Polyester (virgin) is used across many sectors:
-
Apparel (sportswear, outerwear, blends).
-
Home textiles (curtains, upholstery).
-
Industrial fabrics (belting, ropes).
-
Packaging (films, trays).
-
Bottles and containers.
rPET fiber is common in:
-
Apparel (t-shirts, fleece, knitwear).
-
Fillings (pillows, sleeping bags).
-
Carpets and rugs.
-
Nonwovens (wipes, insulation).
-
Some technical textiles when quality is controlled.
Brands often choose rPET to show sustainability credentials. But rPET must meet the product’s technical needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between rPET and polyester fiber?
The biggest difference lies in their raw materials. Polyester fiber is made from virgin petroleum-based PET, while rPET fiber is produced from recycled PET waste like plastic bottles.
Is rPET fiber sustainable?
Yes. rPET reduces plastic waste, lowers energy use during production, and supports circular economy practices, making it far more sustainable than virgin polyester.
Does rPET fabric last as long as polyester fabric?
In most cases, rPET fabric performs almost identically to traditional polyester fabric material. Both are durable and versatile, with only minimal variations depending on the recycling process.
Can rPET replace polyester in all applications?
Not entirely some high-performance applications may still require virgin polyester. However, rPET can replace polyester in the majority of clothing, packaging, and furnishing uses.
Conclusion
Choosing between rPET fiber and polyester fiber comes down to priorities. If cost and large-scale availability are the focus, polyester remains dominant. But if sustainability and waste reduction matter, rPET provides a powerful alternative without sacrificing performance.
As industries and consumers continue to push for greener solutions, the use of rPET will likely expand, gradually reshaping the future of textiles and packaging. The next time you pick up a polyester fabric material, consider whether it’s made from virgin resources or recycled ones that help close the loop.
At Saheb Fibre, we are committed to driving this transformation by offering high-quality rPET fiber solutions that align with global sustainability goals. Whether you’re a manufacturer, brand, or business looking to reduce your environmental footprint, choosing rPET over virgin polyester is a step toward a greener, more responsible future.